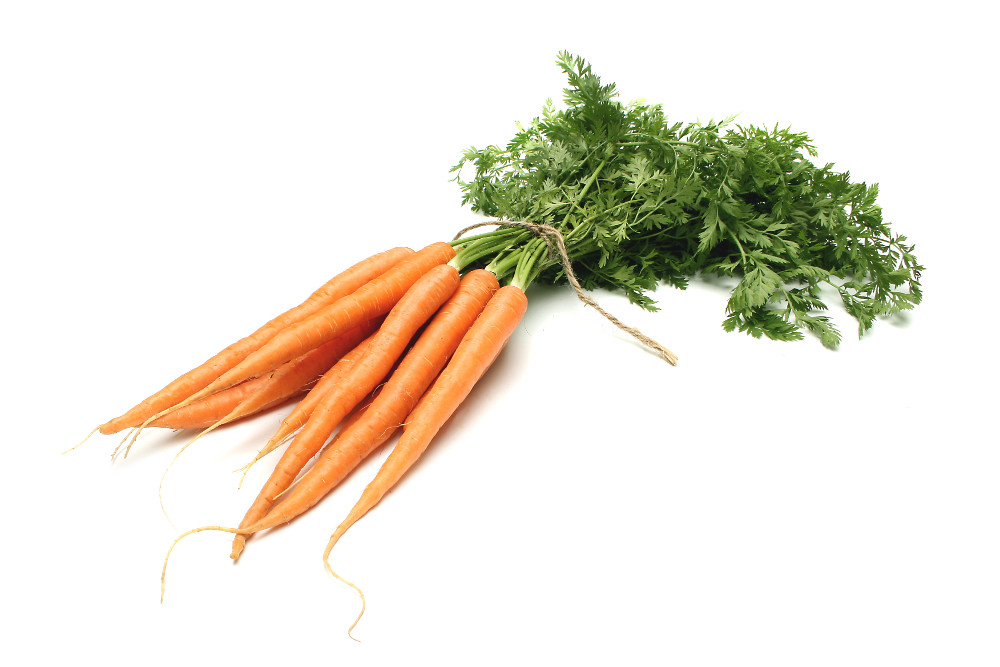
The carrot gets its characteristic, bright orange colour from β-carotene, and lesser amounts of α-carotene, γ-carotene, lutein and zeaxanthin. α and β-carotenes are partly metabolized into vitamin A, providing more than 100% of the Daily Value (DV) per 100 g serving of carrots. Carrots are also a good source of vitamin K (13% DV) and vitamin B6 (11% DV), but otherwise have modest content of other essential nutrients
Carrots can be eaten in a variety of ways. Only 3 percent of the β-carotene in raw carrots is released during digestion: this can be improved to 39% by pulping, cooking and adding cooking oil. Alternatively they may be chopped and boiled, fried or steamed, and cooked in soups and stews, as well as baby and pet foods.